Table of Contents

Riveting vs Welding! Discover the best connections for your business. And enhance the security of your program with the right connectivity solution. Learn more!
Do you understand the difference between riveting and welding? Have you suffered financial losses due to incorrect connections? This is because you have not properly understood and selected riveting and welding.
Table of Contents
What is Riveting?

Riveting is a mechanical joining process used to permanently secure two or more materials together. It is usually done using a rivet, which is a cylindrical metal fastener with a cap head on one end.
The process of riveting usually involves the following steps:
- Preparing the material: The material to be joined is prepared by drilling holes in predetermined locations. The size and location of the holes may vary depending on the specific application and the type of rivet used.
- Inserting and installing the rivet: The rivet is inserted through the hole in the material. The uncapped end of the rivet, called the tail, protrudes through the back of the material. Using specialized tools, the tail of the rivet is deformed or compressed and forms a strong and permanent connection between the materials.
Riveting is widely used in applications that require high strength, vibration resistance and permanence of the connection. It is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction and shipbuilding.
Types of Riveting Joints
The riveted joints have different designs. They are often selected as the appropriate design based on the assembly of the riveted joint, design considerations, and conditions of use. We can make a simple categorization. According to the number of rows and arrangement of rivets can be divided into the following two types.
- Lap Joint
- Butt Joint
1.Lap Joint
Lap joints are two overlapping materials joined together by rivets. This type of riveted joint is usually used when there is a need to overlap one material on top of another. An example would be the joining of sheet metal. The diagram on the right shows how Lap Joint, a type of riveted joint, is represented.
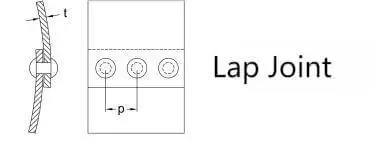
2.Butt Joint
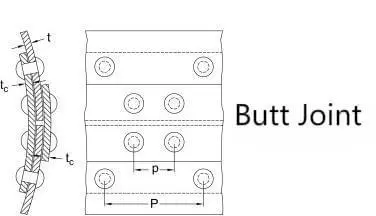
Butt Joints are often required to join three pieces of material. This type of riveted joint joins the ends of two materials together and then uses rivets to secure them.Butt Joints are often used in structural applications where a flush and strong joint is required. The diagram to the left clearly illustrates the connection characteristics of the Butt Joint.
Pros and Cons of Riveting
Pros
- High Strength: Riveting provides a very strong connection that can withstand high loads and resist vibration. The deformation and expansion of the rivet makes the connection stronger with good tensile and shear strength.
- Permanent Connection: Riveting is a permanent connection method where the rivets do not tend to loosen or come loose, providing a lasting connection. This makes riveting useful in applications that require stable and reliable connections, such as structural and mechanical assemblies.
- Corrosion Resistance and Durability: Rivets are often made from corrosion resistant materials such as stainless steel or aluminum alloys, allowing them to be used in harsh environments and have a long service life.
- Weight Savings: Riveting typically provides a lighter weight connection compared to other joining methods such as welding. This is important for applications that require weight reduction, such as the aerospace and automotive industries.
- Automatizable: Riveting can be mass-produced with automated tools and machines, increasing productivity and consistency. This makes riveted joints ideal for mass production.
Cons
- Non-removable: The connection created by riveting is permanent and cannot be easily removed or adjusted.
- Visibility: Rivets may be less prominent in appearance than other joining methods such as bolts. This can be a disadvantage in some applications, particularly where a fine appearance or ease of inspection is required.
What is Welding?

Welding is a process of joining metals to each other by heating and melting the materials. In welding, two or more metal workpieces are heated to a high enough temperature to melt them and form a strong joint when cooled.
The basic principle of welding is to partially melt the surfaces of the metal workpieces by providing heat energy and forming a permanent joint in the molten state. Welding rods, wires or fluxes are usually used as filler materials which fill the weld during the melting process and add strength and stability to the connection.
The welding process usually consists of the following steps:
- Preparing the Workpiece: The metal workpiece to be welded needs to be cleaned and prepared to ensure a quality welded joint. This includes removing oxides, dirt and coatings from the surface.
- Heating and Melting: Using welding equipment, such as an arc welder, gas welder or laser welding equipment, the area of the welded joint is heated to a temperature high enough to melt the metal.
- Filler Material: A suitable filler material, such as welding rod or wire, is added to the melted metal joint. The filler material melts and fills the weld, adding strength to the joint.
- Cooling and Curing: After the welding process is complete, the weld cools and cures to form a strong joint. The cooling time depends on the materials and processes used in the welding process.
Welding can be used to join different types of metals such as steel, aluminum, copper, and stainless steel. It is widely used in manufacturing, construction, automotive industry, aerospace industry etc. Welding provides strong connections characterized by high strength, durability and vibration resistance.
However, welding requires specialized knowledge and skills of the operator and compliance with relevant safety measures as it involves high temperatures and flames. In addition, welding has some limitations, such as the distortion produced during the welding process, the sensitivity of the welded joints and the difficulty of welding specific materials.
Types of Welding Joints
Butt Joint: A butt joint is formed when the ends of two workpieces are aligned in the same plane and welded together along the seam. This is one of the most common types of joints in welding.
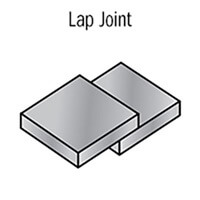
Lap Joint: In a lap joint, one workpiece overlaps the other, and welding is done along the overlapping region. Lap joints are often used for joining sheet metal or thin materials.
T-Joint: A T-joint is formed when one workpiece is placed perpendicularly to the other, creating a T-shape. Welding is done along the intersection of the two pieces. T-joints are commonly used for connecting two materials at a right angle.
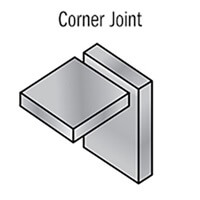
Corner Joint: Corner joints are formed when two workpieces meet at a corner, and welding is done along the corner. This type of joint is commonly used in box-like structures or frames.
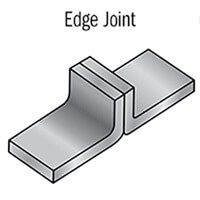
Edge Joint: An edge joint is formed when the edges of two workpieces are placed in contact with each other and welded along the edge. This joint is often used for joining plates or panels.
Pros and Cons of Welding
Pros
- High Strength: Welding provides a very strong connection and the strength of a welded joint can often approach or reach the strength of the weld metal. This makes welding ideal for many applications, especially where high loads and resistance to vibration are required.
- Durable Connections: Welding is a permanent joining method in which the welded joint is not prone to loosening or unraveling, providing a durable connection. This connection is very robust and reliable in structural and mechanical assemblies.
- Adaptable to various shapes and sizes: welding can be adapted to workpieces of various shapes and sizes. Whether it is a thin plate, a pipe, an angle iron or a complex structure, welding provides a flexible connection.
Cons
- Specialized skills required: Welding requires specialized knowledge and skills, and operators need to be trained and equipped with proper welding techniques. Incorrect welding practices may result in weakened welds, distortion or other welding defects.
- Distortion and Stress Concentration: Heat affected zones during the welding process may result in distortion of the workpiece and stress concentration near the joint. This may affect the shape and performance of the workpiece and require compensating measures.
- Welding costs: Welding equipment and materials are relatively expensive, especially for some special welding processes and requirements. In addition, welding requires additional time and labor costs.
- Requirements for access space: Welding typically requires access to the welded joint on both sides, which can be limited for some space-constrained applications.
Differences Between Welding and Riveting
| Welding | Riveting | |
| Strength | Ideal for applications where extreme forces are required | Enabling them to withstand high forces |
| Fatigue Resistance | Poor fatigue resistance | Better fatigue resistance |
| Disassembly and Repair | Difficult to disassemble and repair | Easily disassembled |
| Temperature Effects | May cause problems such as deformation of the material and changes in properties in the heat affected area. | There is no effect on the heat treatment or properties of the material |
| Corrosion Resistance | May cause galvanic corrosion problems | High corrosion resistance |
| Manufacturing Cost and Complexity | High cost | Low cost |
| Design Flexibility | Suitable for straight structures and flat joints | More flexible in design |
How Strong is Riveting?
Riveting is a very strong and reliable connection. But different types of rivets have different strengths.
The strength of a riveted joint will vary depending on the type of rivet, the material being joined and the design of the joint. For example, solid rivets are much stronger than blind rivets. That is why solid rivets are widely used in heavy duty applications.
However, the strength of rivets cannot be compared to welding. In some applications where very high joint strength is required, welding or other techniques may be preferred. In many structural and non-structural applications, riveting can still provide strong and durable joints when properly designed and executed.
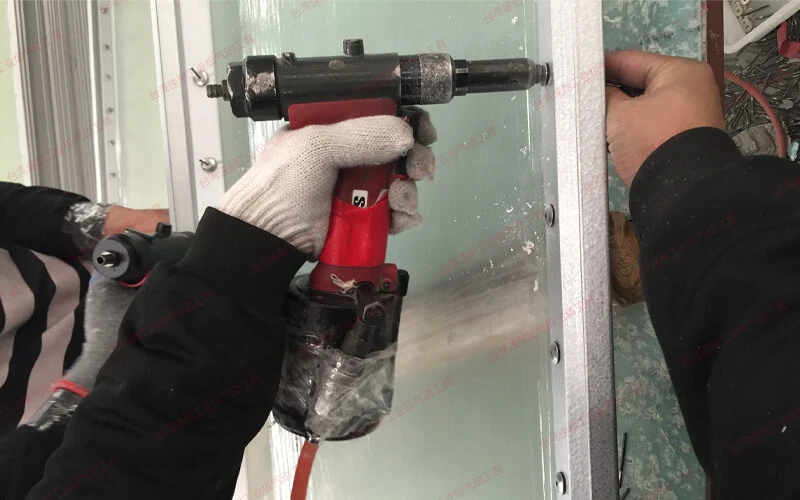

Is Riveting Stronger than Welding?
The strength of riveted versus welded joints depends on a variety of factors, including the specific application, the materials being joined, and the design of the joint. In general, welding typically provides a stronger and more continuous joint strength than riveting.
Welding typically results in fusion of the base material, creating a continuous joint of similar or nearly similar strength to the parent material. This fusion provides excellent load carrying capacity and resistance to shear and tensile forces. Riveted joints, on the other hand, rely on the mechanical locking of the rivet to the material being joined. While riveted joints can be strong, their strength depends on the specific design and the strength of the rivet itself.
Is Welding Cheaper than Riveting?
In practice, welding is more costly than riveting.
- Welding usually requires specialized equipment such as welding machines, power sources, welding guns and protective gear. The economic investment in welding equipment may be higher compared to that required for riveting.
- Consumables such as welding rods, wires, shielding gases and fluxes are usually used in the welding process. These consumables may increase the total cost of welding.
- The operation of welding requires skilled welders who must be properly trained and certified. This is especially true for complex or large projects. Welding may also require additional time and effort for setup, positioning, and post-weld processing (such as grinding and finishing). So the labor cost of welding is also high.
Why are Aircraft Riveted and not Welded?
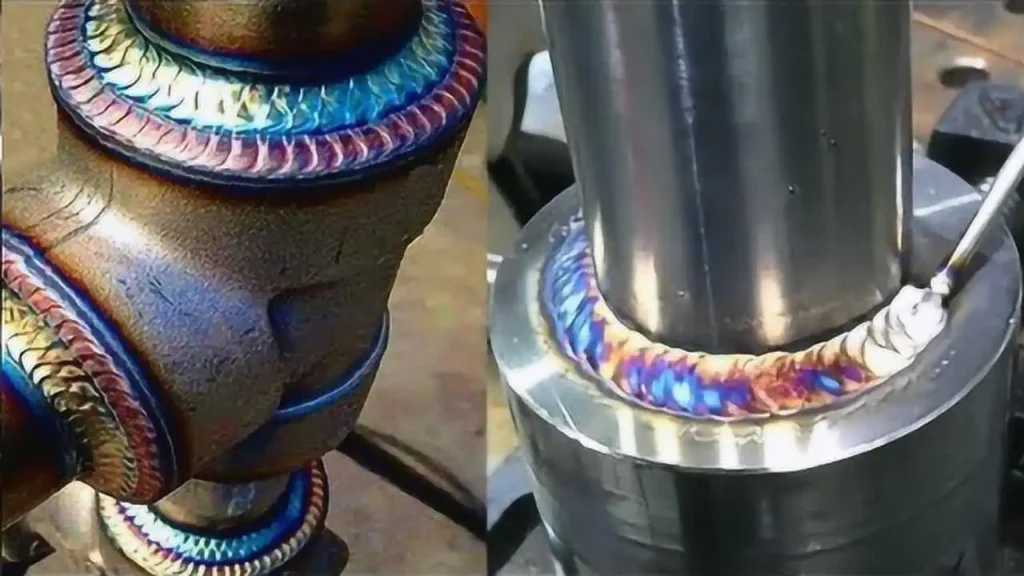


Riveting is often preferred over welding in the construction of airplanes. Riveting is more popular in airplanes as they generally seek lighter weight and greater resistance to vibration. There are several reasons why riveting is chosen for airplanes:
- Riveting can achieve a lighter structure compared to welding. In aircraft design, weight reduction is critical to achieving optimum performance and fuel efficiency. Riveted joints have a smaller overlap and do not require the extra material (e.g. welds) that welded joints do, thus reducing the weight of the overall structure.
- Riveted joints are better able to resist cyclic loading and vibration, which are common in aircraft operations.
- Riveted joints offer the advantage of easy disassembly and repair. In aircraft maintenance, it is often necessary to access internal components or replace damaged sections. Riveted joints can be easily drilled and replaced, whereas welded joints require cutting and re-welding, which is more time-consuming and expensive.
- Riveting allows for more flexible joint design, especially when curved or complex shaped aircraft components are involved. It can better accommodate structural changes and does not require precise alignment during assembly.
- Welding involves high temperatures that may affect the heat treatment and material properties of aircraft alloys. Riveting, on the other hand, does not introduce the same level of heat and thermal distortion.
It is important to note that although riveting is the primary joining method in aircraft manufacturing, welding may still be used in certain specific applications or for specific aircraft components. For example, welded joints are often used in areas where high strength is required, such as engine mounts or landing gear attachment points. Overall, however, riveting offers several advantages in terms of weight, fatigue resistance, repairability and design flexibility, making it the preferred method of aircraft assembly.
Conclusion
Riveting and welding are both commonly used joining methods. Different connection methods should be used for different application scenarios. Riveting is used where uniform load distribution, better fatigue resistance and removability are required. Welding, on the other hand, is suitable for situations where ultra-high strength connections are required. Selection of the appropriate method requires consideration of factors such as strength, fatigue resistance, disassembly, and manufacturing cost to ensure the performance and reliability of the connection.
Want to Order Rivets? Rivmate can Help you!
At Rivmate we offer a wide range of riveting options for all your connection needs. We have a dedicated team of technical engineers who can help and consult on your project.
We have everything from standard rivets to high strength structural rivets to make your project surprisingly secure.
So whether you’re looking for a reliable rivet supplier or a customized rivet solution, Rivmate has you covered. Contact us today and let us help you succeed in your business!




