How to Measure Blind Rivets?
Table of Contents
Blind rivets are a very convenient and fast fastener for connectors. In order to ensure that blind rivets are connected accurately, it is important to measure their dimensions and parameters correctly. Do you know how to measure blind rivets? This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide that will teach you how to measure blind rivets accurately. Ensure that your project has the most secure connections possible.
Preparation Before Measuring Blind Rivets
Before measuring blind rivets, you need to prepare the following tools and materials:
- Calipers: for measuring the length and diameter of the blind rivets.
- Thread gauge: for measuring the type of threads of the blind rivet.
- Mold or Measuring Tool: Used to measure the shape of the head of the blind rivet.
How to Measure Blind Rivets?
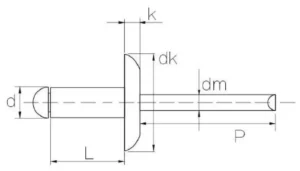
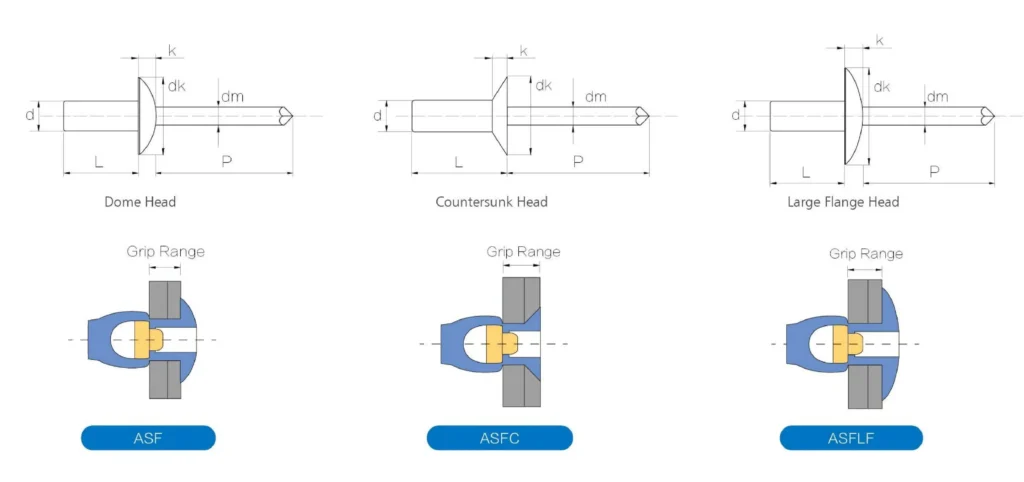
Blind Rivets are generally categorized into three head types – Dome Head, CSK Head, and Large Flange Head. There are some differences in measurements between different head sizes.
Dome Head and Large Flange Head
d : Diameter
L : body length
dk : rivet head dimeter
k : rivet head thickness
dm : mandrel diameter
p : mandrel reveal
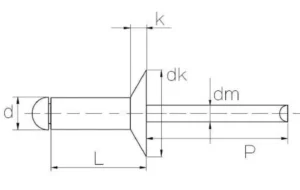
CSK Head (Countersunk Head)
d : Diameter
L : body length
dk : rivet head dimeter
k : rivet head thickness
dm : mandrel diameter
p : mandrel reveal
After understanding the parameters of blind rivets, let’s learn more about how to measure blind rivets.
How are the Diameters of a Rivet Measured? (d)
The diameter of the blind rivet is an important parameter that affects the strength of the connection and the selection of the right size. It plays an important role in the strength and robustness of the connection, the effectiveness of the core extraction, material suitability and installation requirements.
When measuring the diameter of a blind rivet, the topmost part of the rivet should be measured, not the mandrel or head width.
The diameter of the blind rivet should be measured several times and averaged. This will help to calculate the correct size of the blind rivet.
Please note that the diameter of blind rivets is usually measured in millimeters (mm).

How to Measure Rivet Length ? (L)
Selection of the appropriate blind rivet length ensures the range of connections, penetration capability, core pulling effect and safety of the installation, resulting in a high quality connection. The length of the Blind Rivet varies depending on the use and requirements.
When measuring the length, you need to keep the surface of the blind rivet clean and perpendicular to the measuring tool. You need to select the appropriate Blind Rivet length. A blind rivet that is too long may fail to install or cause damage to the material being installed or to objects behind the hole.

How to Measure Rivet Head Diameter ?
The rivet head of a blind rivet provides support and retention, transfer of load, reinforcement of the connection, and cosmetic protection during the joining process. Choosing the right rivet head ensures a quality, reliable and durable connection.
There are three general head shapes for blind rivets: countersunk head, round head and large flange head. In most cases, round head blind rivets will fulfill the requirements of the application. Large flange head blind rivets are used where greater support and load carrying capacity is required. And countersunk head blind rivets are suitable for applications that require a flat, bump-free joint surface. When selecting a head type, it is important to consider the requirements of the connection, the nature of the material, and the desired support and appearance.

Differences in Blind Rivet Threads
Blind Rivets have different threads depending on the application. The internal threads of a blind rivet are usually located at the bottom of the rivet. It can accept threaded bolts or nuts for a stronger connection. Internally threaded blind rivets are typically used in applications that require a removable connection.
The external threads are usually located on the top of the rivet. Capable of accepting nuts or other threaded connectors for a stronger connection. Externally threaded blind rivets are typically used in applications where additional holding force is required during the joining process or where they need to be used in conjunction with other threaded connectors.
Grip Range of Blind Rivets
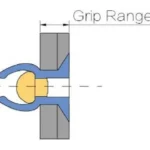
The grip range of a blind rivet is the range of thicknesses of plates or connections it can join. It indicates the distance between the minimum and maximum thickness of the material that a blind rivet can grip.
The grip range is an important parameter. If the grip range of a blind rivet exceeds the thickness range of the material to be joined, the connection may fail or not achieve the required strength and reliability.
Typically, the length of the blind rivet and the core length (the length of the blind rivet sticking out of the sheet) affects the range of its grip range.
When selecting a blind rivet, it is necessary to determine the appropriate grip range of the blind rivet based on the thickness of the material to be joined.
How do I Know My Rivet Size ?
Blind Rivets are typically sized by diameter, length and core length. When approaching the blind rivet business, you will often see numbers such as 1/8″, 1/4″, etc., which represent the diameter of the blind rivet. Take a 1/8″ (0.125 inch) blind rivet as an example to explain how to determine the size of a blind rivet:
Diameter: The diameter of a blind rivet is usually expressed in inches or millimeters. 1/8″ blind rivets, indicates a diameter of 1/8″ or 3.175 mm.
The conversion of inches to millimeters can be done very simply by following the formula. (mm = in/0.039370)
A complete description of a rivet requires knowing its rivet body length in addition to its diameter. A 3.0 x 6.0 is used as an example for illustration.3.0 means the diameter of the blind rivet is 3.0mm, or 7/61″ inch. 6.0 means Body Length is 6.0-7.0mm length.
With the above information, you will have a complete representation of the size of the rivets.
Rivet Hole Size Chart
To achieve a tight joint, in addition to the rivet size selection being important, the rivet hole is also critical. After determining the rivet size, the hole size must be marked for drilling. Generally, the diameter of the rivet needs to be slightly smaller than the diameter of the hole. This allows the rivet to be inserted without any obstacles, maximizing the gap filling and achieving a tight connection.
Rivet Size and Drill Size
| Rivet Diameter | Hole Diameter Size | |
| Min | Max | |
| 2.4(3/32") | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| 3.0(7/61") | 3.1 | 3.2 |
| 3.2(1/8") | 3.3 | 3.4 |
| 4.0(5/32") | 4.1 | 4.2 |
| 4.8(3/16") | 4.9 | 5.0 |
| 5.0(6/32") | 5.1 | 5.2 |
| 6.0(15/64") | 6.1 | 6.2 |
| 6.4(1/4") | 6.5 | 6.6 |
FAQs
How to Measure Rivet Length?
The length of the rivet refers to the total length from the bottom of the rivet head to the tail end of the rivet body, excluding the part of the core shaft pull rod. When selecting the type, it should be calculated based on the total thickness of the two layers of materials (Grip Thickness):
Recommended formula: Length of rivet ≈ Total thickness of material + 1.5 × Diameter of rivet. Ensure that the length of the rivet is sufficient to achieve expansion locking, but do not make it too long to avoid affecting the appearance.
Grip Range refers to the range of material thickness that the rivets can firmly grip. It is usually indicated in the product specifications (for example: 3.0–5.0 mm). If the thickness of the connecting material exceeds this range, the rivets cannot fully expand and lock securely; conversely, if the thickness is too thin, the rivets will be pulled out and the connection will be unstable.
Rivmate suggests: The material thickness should be as close as possible to the middle value within the Grip Range to achieve the best riveting strength.
What Hole Size Should I Drill?
The aperture should be slightly larger than the diameter of the rivet body to allow insertion without any obvious gap. Generally, it is recommended that the aperture size be equal to the rivet diameter plus 0.1–0.2 mm. For example: 4.8 mm rivet → The recommended aperture size is 4.9–5.0 mm.
Which Head Style Should I Use?
Blind rivets can be selected with different head types depending on their application:
- Dome Head: The most versatile option, suitable for metal plate connections.
- Countersunk Head: Suitable for smooth surfaces, such as car exteriors.
- Large Flange: Used for soft materials or in situations where pressure dispersion is required.
The choice of hairstyle not only affects appearance, but also relates to the distribution of force and the tensile strength.
How to Ensure Accurate Measurement?
Before measurement, please ensure:
- Use a vernier caliper or digital caliper to measure the diameter and length;
- Remove burrs at the edge of the holes to prevent dimensional errors;
- Check the flatness of the rivet head to ensure consistent measurement points.
In mass production, the Rivet Gauge provided by Rivmate can be used for quick inspection to ensure consistency and assembly efficiency.
Choose Rivmate Blind Rivet Solutions

Accurate measurement of Blind Rivets is not only the first step in selection, but also a crucial step to ensure the structural stability and product reliability. By precisely determining the diameter, length, grip range, and hole diameter, you can significantly improve the assembly accuracy and avoid problems such as loosening, cracking, or insufficient strength.
Contact us to obtain the blind rivet measurement guide, specification comparison table and professional selection suggestions. Rivmate will provide you with high-precision, standardized fastening solutions, ensuring that every riveting is more stable, stronger and more efficient.
Reference

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met



