Types of Pop Rivets: The Complete Guide to Pop Rivets
Table of Contents
Pop Rivets are widely used in sheet metal processing, home appliance assembly, automotive manufacturing, and aircraft structures. The correct selection of different types of Pop Rivets is crucial for improving assembly quality, reducing rework rates, and extending the service life of products. This article will comprehensively analyze the types of Pop Rivets and provide you with a practical and complete selection guide. Rivmate has long served various OEMs and industrial users, maintaining industry leadership in product development, material selection, and customer support. This guide will help you make more efficient and reliable selection decisions in actual projects.
What Are Pop Rivets and How Do They Work?
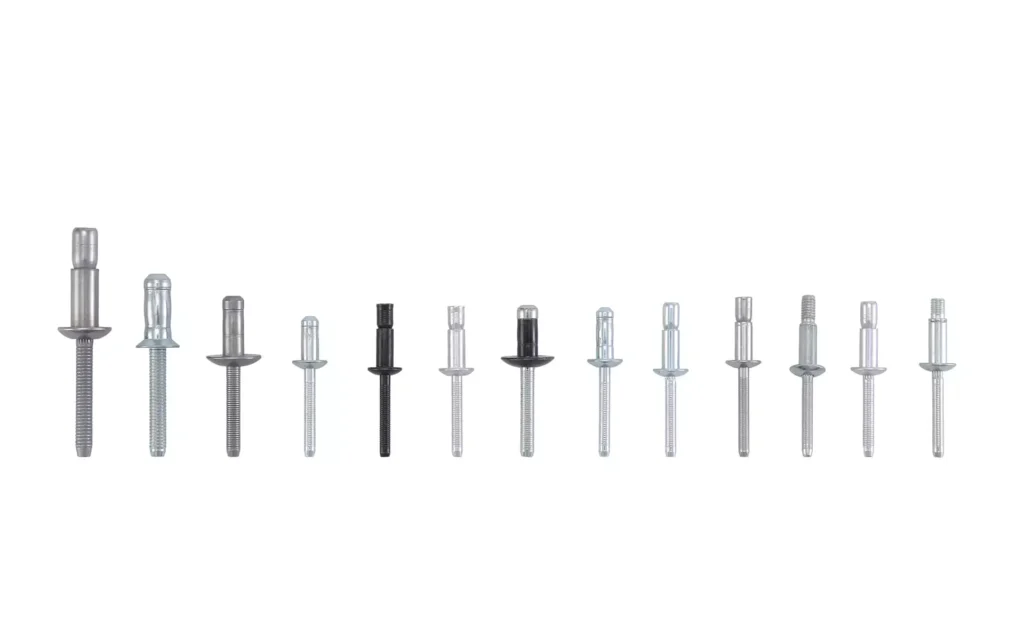

A pop rivet, often referred to in Chinese as a draw rivet or blind rivet, is a fastener commonly used to join two or more material workpieces. Its notable feature is that it does not require access to the back of the workpiece during installation, making it highly suitable for confined spaces or single-sided operations. This characteristic has led to its widespread application in modern industrial assembly.
The basic structure of a blind rivet consists of a head (shell) and a mandrel (pull rod). During installation, a specialized riveting gun is used to pull the mandrel, causing the tail of the mandrel to expand the head and form a locking structure on the back of the material. Eventually, the mandrel breaks at a predetermined position, creating a secure connection point. The entire process does not require welding, threaded engagement, or nut support.
Compared with traditional screws, Pop Rivets offer greater vibration resistance and faster installation speed. Compared with welding, it does not require high-temperature operations or surface treatment, and is safer and more suitable for joining different materials. Especially when connecting thin-walled parts such as aluminum plates, stainless steel plates, plastic parts, and composite materials, Pop Rivets provide a reliable and efficient solution. According to market research in 2024, more than 65% of thin plate connection applications still prefer blind rivet structures.
Main Types of Pop Rivets
- Material Compatibility: Suitable for most common metal materials such as aluminum, carbon steel, stainless steel, etc., and also compatible with certain hard plastics. It is recommended for low-load connections between homogeneous or heterogeneous metals.
- Advantages: Simple structural design, low production cost. Installation speed is fast. It is the most widely used type of rivet on the market. Multiple sizes and material combinations are available, with strong adaptability.
- Limitations: The core shaft tail is exposed after riveting, and the back is open, making it impossible to achieve waterproof sealing. It is not recommended for use in sealed or high-protective-grade equipment.
- Typical Application Scenarios: Lightweight metal frames, ventilation ducts, appliance panels, signboards fixation, maintenance assembly.
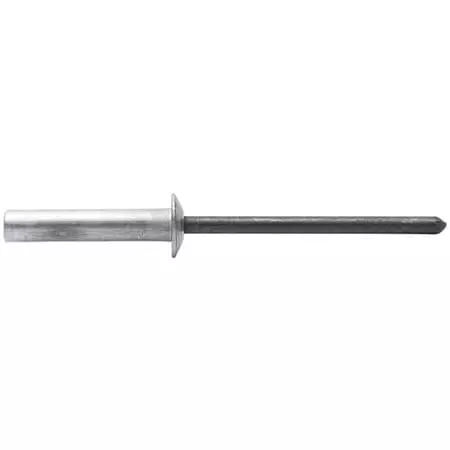


- Material Compatibility: Preferentially adopts metal-to-metal connection, particularly suitable for aluminum and stainless steel combinations. It performs exceptionally well in environments with high waterproof and dustproof requirements.
- Advantages: The tail end of the cap body is designed with a sealing mechanism, effectively preventing water, oil or gas from penetrating. After the core shaft breaks, it is completely enclosed within the rivet, enhancing the anti-shear and anti-vibration performance. Some models have air-tightness certification.
- Limitations: The structure is complex and the unit price is high. There are certain requirements for the matching of installation tools, and the breaking force of the core shaft needs to be precisely controlled.
- Typical Application Scenarios: Automotive chassis components, waterproof wiring boxes, outdoor electronic devices, ship equipment assembly, industrial electrical cabinets.
- Material Compatibility: Suitable for various metal and plastic combinations for assembly, particularly suitable for flexible production environments with frequent thickness variations.
- Advantages: One specification covers multiple clamping thicknesses, significantly reducing the number of inventory SKUs. The core shaft locking mechanism is stable and adaptable to installation tolerance fluctuations.
- Limitations: Due to the wide compatibility range, the single-point clamping force is not as precise as that of dedicated specifications. Caution should be exercised when using it in parts with high structural strength requirements.
- Typical Application Scenarios: Equipment after-sales maintenance, rapid assembly at service stations, multi-specification assembly lines of OEM manufacturers, and assembly stages of non-standard equipment.
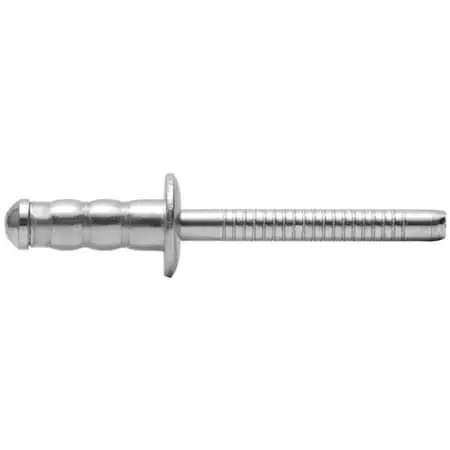
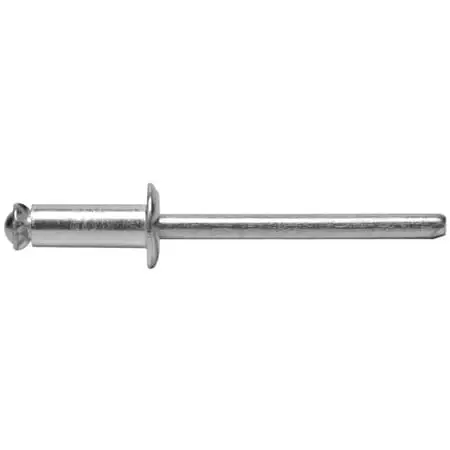


- Material Compatibility: Recommended for soft materials such as plastic sheets, plywood, fiberglass boards, etc., and also suitable for thin metal component combinations.
- Advantages: The core shaft splits into multiple “petals” during the pulling process, creating a wider back support surface to prevent the soft material from tearing. This can enhance connection stability and surface integrity.
- Limitations: The shear and tensile strength is not high, making it unsuitable for load-bearing parts or connections between structural components. The petal structure may interfere with the space behind.
- Typical Application Scenarios: Household items, soft plastic products, lightweight interiors, composite board assembly, thin-walled furniture connections.
- Material Compatibility: Specifically suitable for wood, concrete, gypsum board, and other porous or low-density materials. Not recommended for metal sheets.
- Advantages: The outer part of the cap has spiral or vertical grooves, which can achieve mechanical embedding fixation in soft or porous substrates, forming a stronger frictional bonding force.
- Limitations: Pre-installed holes must match the material properties, and installation requires moderate force control. There is a high risk of surface damage, and it is not recommended for use in finished interior areas.
- Typical Application Scenarios: Custom wooden furniture, assembling floor joists, building material fixation, woodwork structure construction, interior wall panel reinforcement.


- Material Compatibility: Suitable for high-load metal structures, such as thick steel plates, stainless steel brackets, and industrial aluminum profiles.
- Advantages: Specifically designed for heavy-duty structures, it boasts extremely high shear and tensile strength. The core shaft locking mechanism ensures that the screws do not loosen, and it is often used as an alternative to welding or bolts. It has vibration resistance capabilities and is suitable for dynamic load environments.
- Limitations: Requires the use of high-tension tools and standardized installation procedures. The accuracy of the processing hole positions must be strictly controlled.
- Typical Application Scenarios: Commercial vehicle frames, rail transit equipment, wind power structural components, bridge maintenance supports, and steel structure node connections.
- Material Compatibility: Suitable for soft plastics, composite materials, foam-backed structures, and also for non-structural decorative parts.
- Advantages: After the core shaft is pushed forward, the tail end expands into three sections, like an “umbrella” unfolding, significantly increasing the back surface area to protect the soft materials from indentation damage. Suitable for areas with high appearance requirements.
- Limitations: The structure is complex and the cost is relatively high. The connection strength is moderate and not suitable for load-bearing nodes.
- Typical Application Scenarios: Automotive interior panels, plastic casings, cable supports, medical equipment shells, lightweight decorative panels.

Types and Properties of Materials

When choosing Pop Rivets (pull rivets), the selection of the material not only affects the mechanical properties of the connection components, but also directly relates to the durability, environmental adaptability and overall cost control of the product. Pull rivets usually consist of two parts: the socket (cap body) and the core shaft. The material combination of these two parts must be coordinated to ensure a stable and reliable riveting process. The following are comparisons and application suggestions for several common materials:
- Characteristics: Lightweight, with moderate strength and excellent corrosion resistance.
- Advantages: Light in weight, suitable for structures that are sensitive to total weight. Resistant to oxidation, suitable for outdoor or humid environments.
- Limitations: The strength is lower than that of steel, and the bearing capacity is limited.
- Recommended Usage: Aviation aluminum plates, appliance housings, bicycle parts, vehicle body trim.
- Features: High strength, good rigidity, low price.
- Advantages: Strong against shear force, suitable for high-load structural connections. Good economic performance.
- Limitations: Prone to rust, requires surface galvanization or coating treatment. Not recommended for corrosive environments.
- Recommended Usage: Industrial machinery, steel structures, sheet metal cabinets, bracket supports.
- Characteristics: Extremely strong corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
- Advantages: Suitable for harsh environments such as high humidity, high salt content, and high temperatures. No additional treatment is required on the surface, and the lifespan is long.
- Limitations: High processing hardness, and installation requires high-tension tools. The cost is higher than that of aluminum and steel.
- Recommended Usage: Ship assembly, outdoor equipment, stainless steel enclosures, railway transportation vehicles.
- Properties: Excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Advantages: Superior in electrical connection. Beautiful appearance with decorative effect.
- Limitations: High price, moderate strength, not suitable for high structural loads.
- Recommended Usage: Electrical grounding connection, architectural decoration, structural components for handicrafts.
5. Matching Mandrel and Shell Materials
- Principle: The core shaft material must have sufficient hardness to complete the riveting action and break at the designated position. At the same time, it should avoid electrochemical corrosion with the cap body material.
- Common combinations:
- Aluminum shell + Steel core shaft: High cost-effectiveness, suitable for general assembly.
- Aluminum shell + Aluminum core shaft: Completely corrosion-resistant, suitable for marine or humid hot environments.
- Stainless steel shell + Stainless steel core shaft: High-strength corrosion-resistant combination, used in high-demand industrial settings.
- Copper shell + Copper core shaft: For applications requiring conductive performance, to avoid potential electrical potential differences between different materials.
How to Choose the Right Pop Rivet
Each type of rivet has its designated grip range. The total thickness of the material must fall within this range; anything outside the range will result in the rivet not forming correctly.
Example: If the total thickness is 3.0mm, it is recommended to use a model with a grip range of 2.5–3.5mm.
2. Rivet Length
The total length of the rivet should be reserved with space considering the thickness of the material and the post-riveting forming height.
Generally, it is recommended that: the length of the rivet = total thickness of the material + expansion length of the core shaft.
3. Tensile and Shear Load Requirements
If the connecting piece is subjected to tensile or shear forces, it is necessary to select materials and structural type rivets with corresponding strength grades. For high-strength applications, stainless steel or structural type (such as Hemlok) rivets are recommended.
4. Environmental Conditions
For outdoor, humid and corrosive environments, stainless steel or all-aluminum rivets should be selected. In marine or chemical environments, to avoid electro-corrosion by foreign materials, an aluminum-aluminum or stainless steel-stainless steel combination can be used.
5. Material Compatibility
Avoid the combination of metals with different potentials to prevent electrochemical corrosion.
Although the combination of aluminum and steel is economical, it poses a higher risk in humid environments.
How to Install Pop Rivets Properly
In industrial assembly and maintenance, the installation quality of Pop Rivets (pull rivets) determines the strength and durability of the connection. Although the riveting operation seems simple, if the process is not strictly followed, problems such as loosening, detachment or uneven stress may occur. The following content will systematically explain the installation tools, standard steps and quality inspection methods for pull rivets, helping you achieve professional assembly results.
Manual Rivet Gun
- Suitable for maintenance, sample trial assembly, and small batch operations.
- Low cost and portable.
- Applicable to aluminum or small-sized rivets.
- The drawback is high operational intensity and low efficiency.
Electric or Pneumatic Rivet Gun
- Suitable for batch production lines and workshop assembly.
- Provides stable tension to ensure consistent core shaft breakage positions.
- Increases efficiency by over 50%, reducing manual fatigue.
- Regular maintenance of air pressure and tension settings is required to prevent poor riveting.
Auxiliary Tools
- Drilling machine or punching tool: Ensure the hole diameter is precise (it is recommended to be 0.1mm larger than the diameter of the rivet).
- Thickness gauge: Confirm the total thickness of the material to be riveted to avoid exceeding the clamping range.
- Protective equipment: It is recommended to wear protective glasses and gloves to prevent injury from the core shaft flying out.
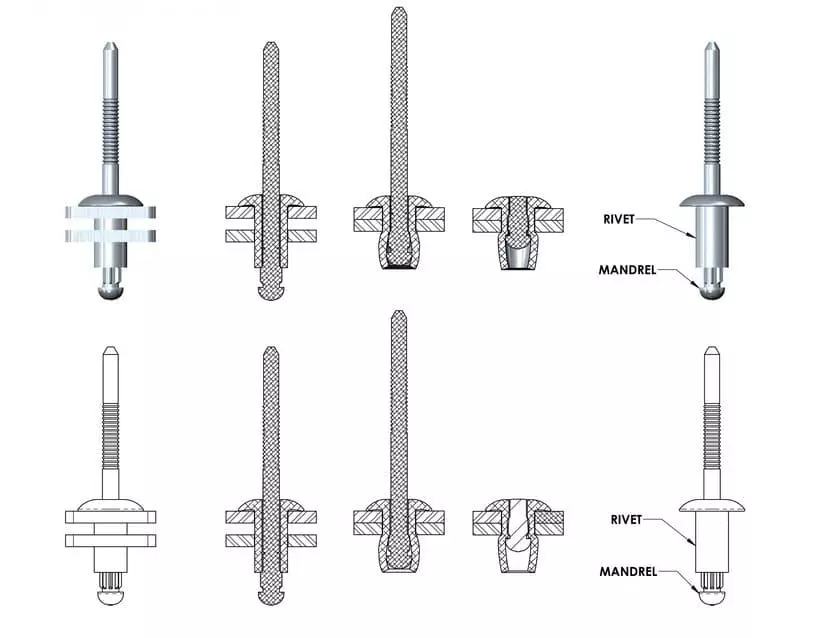
- Drilling the Hole
Drill or punch holes on the connection piece, ensuring that the holes are vertical and clean without any burrs. Make sure the hole size matches the rivet – if it’s too loose, it will come loose; if it’s too tight, it will be difficult to insert. - Insert the Rivet
Insert the rivet cap body into the hole, ensuring that the cap edge is tightly against the surface of the workpiece. Ensure that the rivets are in a vertical position to avoid any skewing that might affect the expansion on the back side. - Engage the Rivet Gun
Insert the nozzle of the riveting gun into the head of the mandrel, and start the riveting process. The core shaft is pulled, and the tail of the cap begins to expand, gradually forming a clamping force. When the core shaft reaches the designed tensile force, it will automatically break and fall off. - Check the joint formation status
After the fracture, check whether the cap body is tightly attached to the surface and whether the expansion on the back is symmetrical. The fracture surface of the core shaft should be smooth and free of obvious residues or protrusions.
Industry Applications of Pop Rivets
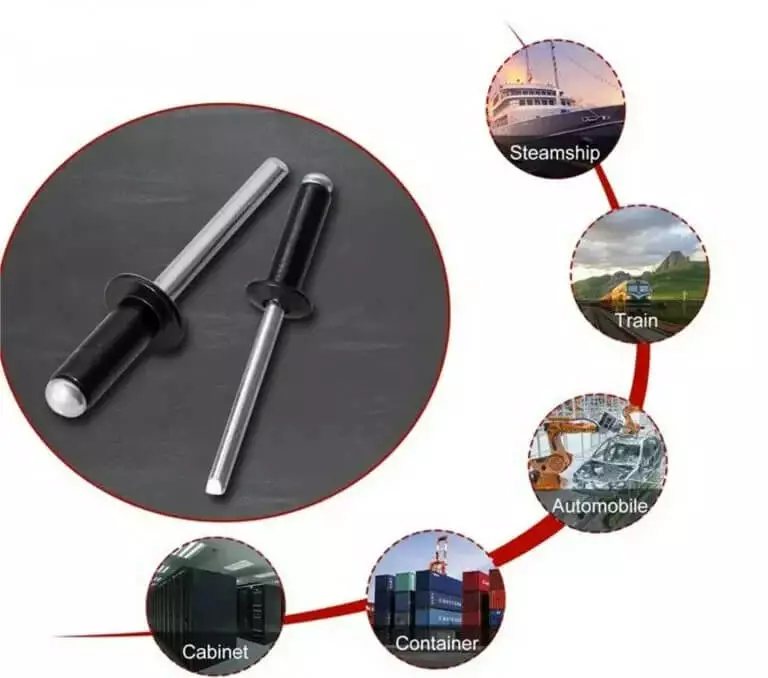

Pop Rivets have become the standard fastening solution in the global assembly industry due to their high efficiency, stability and structural flexibility.
Aerospace Industry
In aircraft structures, lightweighting and safety are the top priorities. Rivmate aluminum and stainless steel rivets are widely used in areas such as fuselage skins, cabin interiors, and cabin door frames. Aluminum Pop Rivets have an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, enabling secure connections while maintaining light weight.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is one of the largest users of blind riveting technology. In the fixation of body panels, chassis, heat insulation shields and interior components, Pop Rivets offer a fast, vibration-resistant and safe connection method. Compared with traditional welding, pull rivets do not require heat treatment or complex fixtures, avoiding metal deformation. They are particularly suitable for aluminum body structures. After corrosion resistance tests (salt spray test for 720 hours), the connection strength and surface integrity both meet the ISO 14589 standards.
Home Appliance & Electronics Assembly
Home appliance assembly emphasizes precision, aesthetics and high efficiency. Rivmate’s open-end aluminum rivets are widely used in products such as air conditioner shells, range hoods, and washing machines. The riveting process does not require welding or nuts, thus avoiding deformation and reducing labor costs.
Construction & Infrastructure
In building curtain walls, metal roofs and steel structure supports, Pop Rivets possess long-lasting weather resistance and strong seismic performance. The structural Hemlok series provided by Rivmate has been used in several large-scale construction projects, including high-rise curtain wall systems, photovoltaic support installations and outdoor advertising structures. Compared to bolt connections, the structural rivets can complete construction more quickly and reduce the risk of loosening.
Ready to Choose the Right Pop Rivet? Explore Rivmate Solutions Today
Among various fastening solutions, Pop Rivets have emerged as the core connection method in the manufacturing and maintenance industries due to their simple structure, efficient assembly, and strong adaptability. From open-type to structural-type, different types of rivets meet the diverse requirements ranging from lightweight assembly to high-strength structures. The correct type of rivet, material, and installation method determine the strength, safety, and lifespan of the final product.
Rivmate Product & Engineering Support
Rivmate not only offers a full range of industrial-grade Pop Rivets, but also provides customers with systematic support services from selection to application:
- Technical Selection Guidance: Recommend appropriate models based on load, thickness, material and environmental conditions.
- Samples and Performance Testing: Provide mechanical verification reports and clamping performance analysis.
- Automation Solutions: Adapt to automatic riveting guns and batch production line equipment.
- After-sales Support and Training: Offer standard process guidance to the factory assembly team.
All of our products comply with international standards such as ISO 15977, DIN 7337, ISO 14589, ensuring stable quality and consistent assembly.
Get in Touch with Rivmate

Whether you are a design engineer, a purchasing staff or a manufacturing manager, Rivmate can offer you professional and reliable fastening solutions.
📧 Product Inquiry: manufacture@world-rivet.com
🌐 Official Website: https://worldrivet.com/
reference

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met



